
ABDOMINAL ULTRASOUND
 Ultrasound imaging, also called ultrasound scanning or sonography, is a method of obtaining images of internal organs by sending high-frequency sound waves into the body. The reflected sound waves' echoes are recorded and displayed as a real-time visual image. No ionizing radiation (x-ray) is involved in ultrasound imaging. An abdominal ultrasound image is a useful way of examining internal organs, including the liver, gallbladder, spleen, pancreas, kidneys, and bladder.
Because ultrasound images are captured in real time, Ultrasound imaging, also called ultrasound scanning or sonography, is a method of obtaining images of internal organs by sending high-frequency sound waves into the body. The reflected sound waves' echoes are recorded and displayed as a real-time visual image. No ionizing radiation (x-ray) is involved in ultrasound imaging. An abdominal ultrasound image is a useful way of examining internal organs, including the liver, gallbladder, spleen, pancreas, kidneys, and bladder.
Because ultrasound images are captured in real time,
they can show movement of internal tissues and organs and enable physicians to see blood flow. This can help to diagnose a variety of conditions and to assess damage caused by illness.
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY
Cardiac ultrasonography (echocardio-graphy) is a valuable non-invasive tool for imaging the heart and surrounding structures. It can be quite helpful in establishing a specific diagnosis and estimating the severity of various cardiac diseases.
VASCULAR ULTRASOUND
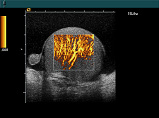
 Ultrasound imaging of the body's veins and arteries can help the radiologist see and evaluate blockages to blood flow, such as clots in veins and plaque in arteries. With knowledge about the arterial blood flow gained from an ultrasound image, the radiologist can often determine whether a patient is a good candidate for a procedure like angioplasty. Ultrasound images may also be used to plan or review the success of procedures that graft or bypass blood vessels-such as renal (relating to the kidney) artery bypass. Ultrasound of the veins may reveal blood clots that require treatment such as anticoagulant therapy (blood thinner), or filters to prevent clots from traveling to the lungs (embolism). Ultrasound of the vascular system also provides a fast, noninvasive means of identifying blockages of blood flow in the neck arteries to the brain that might produce a stroke or mini-stroke. Ultrasound imaging of the body's veins and arteries can help the radiologist see and evaluate blockages to blood flow, such as clots in veins and plaque in arteries. With knowledge about the arterial blood flow gained from an ultrasound image, the radiologist can often determine whether a patient is a good candidate for a procedure like angioplasty. Ultrasound images may also be used to plan or review the success of procedures that graft or bypass blood vessels-such as renal (relating to the kidney) artery bypass. Ultrasound of the veins may reveal blood clots that require treatment such as anticoagulant therapy (blood thinner), or filters to prevent clots from traveling to the lungs (embolism). Ultrasound of the vascular system also provides a fast, noninvasive means of identifying blockages of blood flow in the neck arteries to the brain that might produce a stroke or mini-stroke.
OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY
 Ultrasound scan is currently considered to be a safe, non-invasive, accurate and cost-effective investigation in the fetus. it has progressively become an indispen-sible obstetric tool and plays an important role in the care of every pregnant woman.
Many structural abnormalities in the fetus can be reliably diagnosed by an ultrasound scan, and these can usually be made before 20 weeks. Common examples include hydrocephalus, anencephaly, myelomeningocoele, achondroplasia and other dwarfism, spina bifida, exomphalos, Gastroschisis, duodenal atresia and fetal hydrops.
It has been over 40 years since ultrasound was first used on pregnant women. Unlike X-rays, ionizing irradiation is not present and embryotoxic effects associated with such irradiation should not be relevant. Ultrasound scan is currently considered to be a safe, non-invasive, accurate and cost-effective investigation in the fetus. it has progressively become an indispen-sible obstetric tool and plays an important role in the care of every pregnant woman.
Many structural abnormalities in the fetus can be reliably diagnosed by an ultrasound scan, and these can usually be made before 20 weeks. Common examples include hydrocephalus, anencephaly, myelomeningocoele, achondroplasia and other dwarfism, spina bifida, exomphalos, Gastroschisis, duodenal atresia and fetal hydrops.
It has been over 40 years since ultrasound was first used on pregnant women. Unlike X-rays, ionizing irradiation is not present and embryotoxic effects associated with such irradiation should not be relevant.
|
|